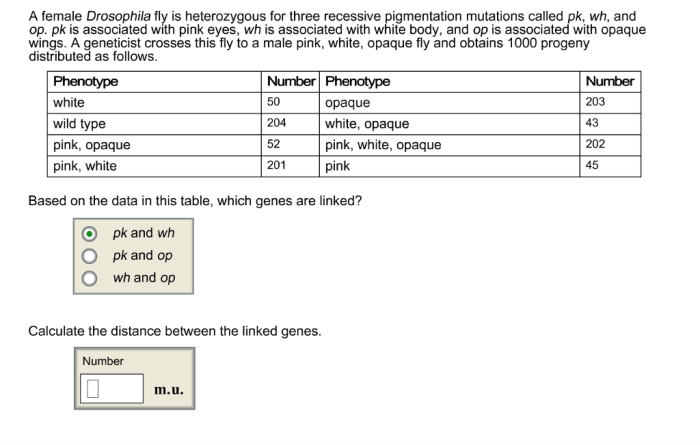
A female drosophila fly is heterozygous – A female Drosophila fly being heterozygous for a sex-linked gene presents a captivating case study in genetics. This condition, where an individual carries different alleles of a gene located on the sex chromosomes, unfolds a fascinating narrative of inheritance patterns and phenotypic variations.
As we delve into the intricacies of this genetic phenomenon, we uncover the fundamental principles governing sex determination and gene expression in Drosophila flies.
Sex chromosomes, the key players in this genetic drama, orchestrate the development of male and female traits. In Drosophila, the X and Y chromosomes hold the genetic blueprints that determine an individual’s sex. Females, endowed with two X chromosomes, inherit a double dose of X-linked genes, while males, with their solitary X chromosome and a Y chromosome, inherit a single copy of these genes.
Heterozygosity in Drosophila Flies: A Female Drosophila Fly Is Heterozygous

Heterozygosity refers to the genetic condition in which an individual possesses two different alleles for a particular gene. Alleles are alternative forms of a gene that occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes. In heterozygous individuals, one allele is inherited from the mother and the other from the father.
The inheritance and expression of alleles in heterozygous individuals depend on the dominance relationship between the alleles. A dominant allele is expressed in the phenotype of the individual even if only one copy of the allele is present. A recessive allele is only expressed if two copies of the allele are present.
Inheritance Patterns of Sex-Linked Genes in Drosophila Flies

Sex chromosomes are chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual. In Drosophila flies, males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY), while females have two X chromosomes (XX).
Genes located on the X chromosome are called X-linked genes, while genes located on the Y chromosome are called Y-linked genes. X-linked genes are inherited differently in males and females due to the difference in the number of X chromosomes.
Inheritance of X-Linked Genes, A female drosophila fly is heterozygous
- Females inherit one X chromosome from each parent, so they can be homozygous dominant (XX), heterozygous (X DX d), or homozygous recessive (X dX d).
- Males inherit one X chromosome from their mother and one Y chromosome from their father, so they can only be hemizygous dominant (X DY) or hemizygous recessive (X dY).
Inheritance of Y-Linked Genes
- Y-linked genes are only present on the Y chromosome, so they are only inherited by males.
- Males inherit one Y chromosome from their father, so they can only be hemizygous for Y-linked genes.
Implications of a Female Drosophila Fly Being Heterozygous for a Sex-Linked Gene
When a female Drosophila fly is heterozygous for a sex-linked gene, she will have one dominant allele and one recessive allele for that gene.
The possible genotypes and phenotypes of her offspring depend on the dominance relationship between the alleles. If the dominant allele is expressed in females, then all of her daughters will express the dominant phenotype, and all of her sons will be hemizygous for the recessive allele and express the recessive phenotype.
If the recessive allele is expressed in females, then all of her daughters will be heterozygous and express the dominant phenotype, and all of her sons will express the recessive phenotype.
Examples of Sex-Linked Genes in Drosophila Flies and Their Effects on the Fly’s Phenotype
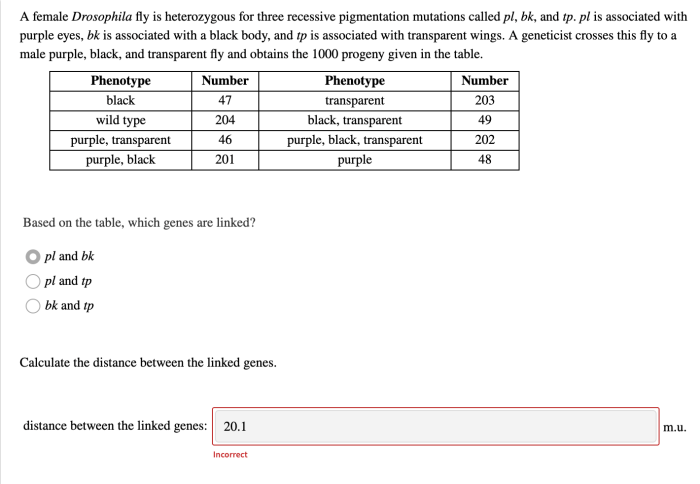
There are many sex-linked genes in Drosophila flies that affect a variety of phenotypic traits.
One example is the white gene, which is located on the X chromosome. The white gene is responsible for eye color, and mutations in this gene can lead to white eyes. Females that are heterozygous for the white gene will have one red eye and one white eye, while males that are hemizygous for the white gene will have white eyes.
Another example is the yellow gene, which is also located on the X chromosome. The yellow gene is responsible for body color, and mutations in this gene can lead to a yellow body color. Females that are heterozygous for the yellow gene will have a yellow body, while males that are hemizygous for the yellow gene will have a white body.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of heterozygosity in a female Drosophila fly?
Heterozygosity allows female Drosophila flies to carry both dominant and recessive alleles of a sex-linked gene, potentially masking the expression of recessive traits.
How do sex chromosomes influence the inheritance of sex-linked genes in Drosophila flies?
Sex chromosomes, particularly the X chromosome in females and the single X chromosome in males, determine the inheritance patterns of sex-linked genes.
What are some examples of sex-linked genes in Drosophila flies and their phenotypic effects?
Examples include the white gene, affecting eye color, and the yellow gene, influencing body color, showcasing the phenotypic variations caused by mutations in sex-linked genes.