Introducing the empirical/molecular formula practice worksheet answers, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of determining and utilizing empirical and molecular formulas, empowering you with a profound understanding of these fundamental chemical concepts.
This guide provides a systematic approach to understanding the differences between empirical and molecular formulas, along with step-by-step instructions for calculating both types of formulas from provided data. Additionally, it explores the practical applications of these formulas in various scientific fields, showcasing their significance in compound identification and characterization.
Empirical and Molecular Formula Practice Worksheet
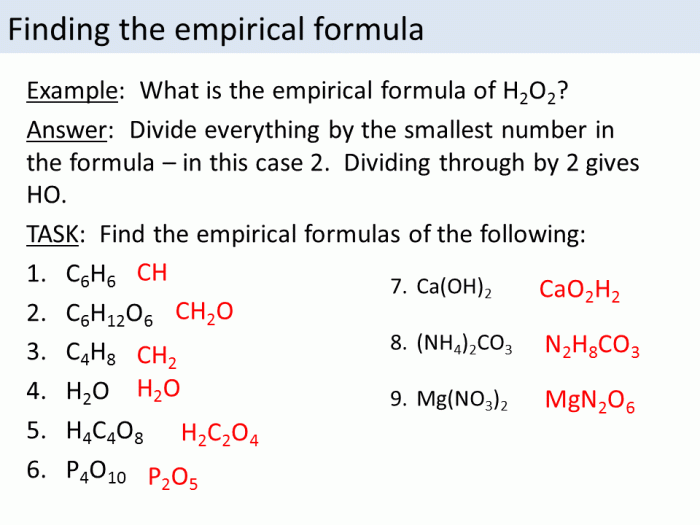
This worksheet provides practice problems and solutions for calculating empirical and molecular formulas. It also includes a brief review of the difference between empirical and molecular formulas.
Empirical Formula
An empirical formula is a chemical formula that shows the relative proportions of the elements in a compound. It does not necessarily represent the actual number of atoms of each element in the compound.
To determine the empirical formula of a compound, you need to know the mass of each element in the compound. Once you have the masses, you can convert them to moles and then divide by the smallest number of moles to get the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements.
Molecular Formula
A molecular formula is a chemical formula that shows the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound. To determine the molecular formula of a compound, you need to know the empirical formula and the molar mass of the compound.
Once you have the empirical formula and the molar mass, you can divide the molar mass by the empirical formula mass to get the molecular formula.
Applications of Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Empirical/molecular formula practice worksheet answers
Empirical and molecular formulas are used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. They are used to identify and characterize compounds, to calculate the molar mass of compounds, and to determine the stoichiometry of reactions.
FAQ Compilation: Empirical/molecular Formula Practice Worksheet Answers
What is the difference between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements present in a compound, while a molecular formula indicates the exact number of atoms of each element in a molecule of the compound.
How do I determine the empirical formula of a compound?
To determine the empirical formula, you need to determine the mass percent of each element in the compound and convert those percentages to moles. Then, divide each mole value by the smallest mole value to obtain the simplest whole-number ratio of elements.
How do I convert an empirical formula to a molecular formula?
To convert an empirical formula to a molecular formula, you need to know the molar mass of the compound. Divide the molar mass by the empirical formula mass to obtain a whole number, which represents the molecular formula multiple. Multiply the subscripts in the empirical formula by this multiple to obtain the molecular formula.


