In the realm of wound care, CPT codes play a pivotal role in billing and reimbursement. One such code is CPT for wound vac change, a procedure that involves replacing the dressing on a wound vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) device. This guide will delve into the intricacies of CPT for wound vac change, providing a comprehensive understanding of its definition, procedure details, billing guidelines, documentation requirements, and infection control measures.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the significance of accurate documentation, the potential complications associated with wound vac changes, and effective troubleshooting techniques. By the end of this guide, you will be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of CPT for wound vac change, ensuring optimal patient care and proper reimbursement.
Definition of CPT for Wound Vac Change
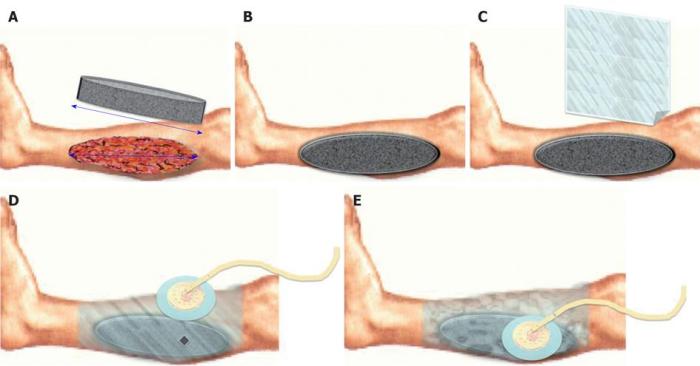
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code for wound vac change is a specific medical code assigned to the procedure of changing a wound vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) dressing.
Purpose of CPT Codes
CPT codes are essential in medical billing, as they provide a standardized language for describing medical procedures and services. This ensures accurate and consistent communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Procedure Details
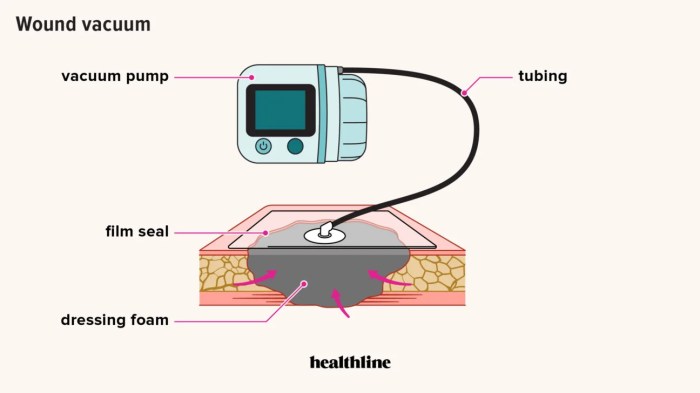
Changing a wound vac involves a series of steps to ensure proper wound care and healing.
The procedure typically includes wound preparation, device application, and thorough documentation.
Wound Preparation
Prior to changing the wound vac, the wound is thoroughly cleaned and debrided to remove any dead tissue or debris.
This helps create a clean surface for the new dressing and promotes optimal healing.
Device Application
The new wound vac dressing is then applied to the wound.
The dressing is typically composed of a foam or gauze pad that absorbs wound exudate, and a transparent film that seals the wound and creates a negative pressure environment.
The negative pressure helps draw out fluids and promote wound healing.
Documentation
After the wound vac is changed, the healthcare professional documents the procedure, including the date and time of the change, the type of dressing used, and any observations or changes in the wound.
This documentation is essential for tracking the progress of the wound and evaluating the effectiveness of the wound vac therapy.
CPT for wound vac change involves utilizing a negative pressure wound therapy device to promote healing. This technique offers various advantages and disadvantages. To learn more about the pros and cons of capta, visit this link . Returning to the topic of CPT for wound vac change, it’s important to consider these factors when determining the appropriate treatment approach for wound management.
Billing and Reimbursement
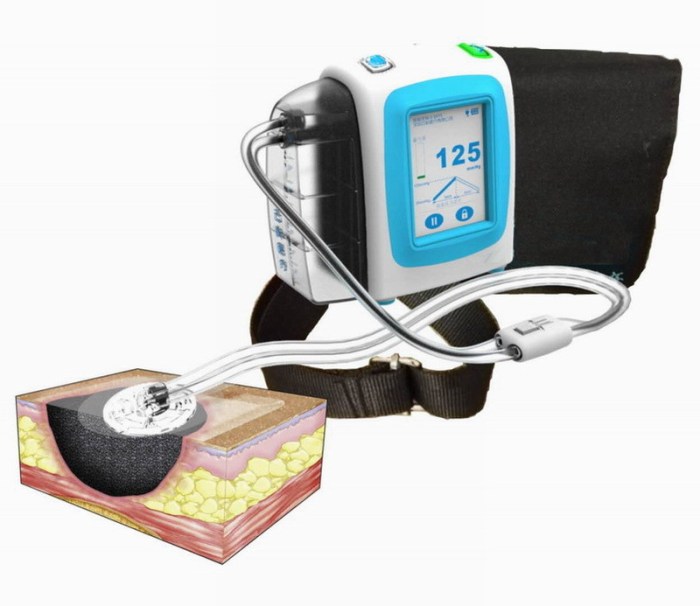
Billing for wound vac changes involves assigning the appropriate CPT codes and understanding the associated reimbursement rates. Accurate documentation is crucial for ensuring proper reimbursement.
CPT Code Selection
- CPT code 97605 is used for initial wound vac placement.
- CPT code 97606 is used for subsequent wound vac changes.
Reimbursement Rates
Reimbursement rates for wound vac changes vary depending on the CPT code and the payer. Medicare’s reimbursement rates are typically lower than those of private insurers.
Importance of Accurate Documentation, Cpt for wound vac change
Accurate documentation is essential for proper reimbursement. The medical record should include the following information:
- Patient’s diagnosis and medical history
- Type of wound vac used
- Frequency of wound vac changes
- Duration of wound vac therapy
Documentation Requirements
Proper documentation is essential for accurate billing and reimbursement of wound vac changes. The medical record should include the following:
- Patient’s medical history and current condition
- Description of the wound, including size, location, and type
- Type of wound vac used
- Frequency and duration of wound vac changes
- Assessment of wound healing progress
- Any complications or adverse events
Photography
Photography can be a valuable tool for documenting wound vac changes. Photographs can provide a visual record of the wound’s appearance and healing progress. They can also be used to support medical decision-making and communication with other healthcare providers.
Complications and Troubleshooting
Wound vac changes, while generally straightforward, can occasionally present complications. Recognizing and managing these complications promptly is crucial to ensure optimal wound healing.
Common complications associated with wound vac changes include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Skin irritation
- Leakage
Troubleshooting and Management
Effective troubleshooting and management of wound vac complications require a systematic approach:
Bleeding
- Apply pressure to the bleeding site.
- Consider using a hemostatic agent.
- If bleeding persists, seek medical attention.
Infection
- Inspect the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Change the wound dressing and tubing as directed by the healthcare provider.
- Administer antibiotics as prescribed.
Skin irritation
- Apply a protective barrier cream or dressing to the surrounding skin.
- Reduce the suction pressure if possible.
- Consider using a different type of wound dressing.
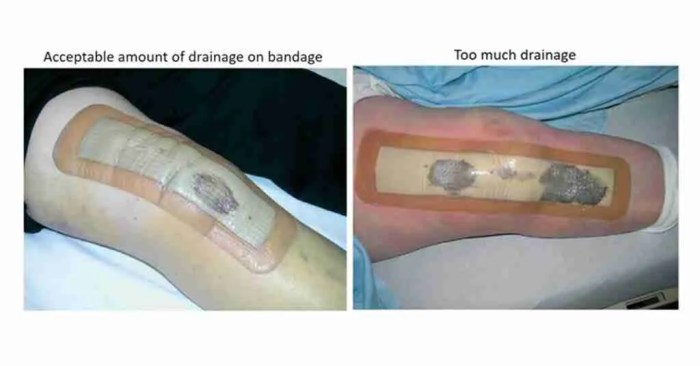
Leakage
- Check the tubing and connections for leaks.
- Replace any damaged components.
- Apply additional dressings or sealants around the edges of the wound.
Infection Control: Cpt For Wound Vac Change
Infection control is paramount during wound vac changes to prevent infection and promote wound healing. Sterile technique is essential, involving the use of sterile gloves, drapes, and instruments. Proper handling of devices is crucial, including regular cleaning and disinfection to minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Preventing and Managing Infections
To prevent infections:
- Assess the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage.
- Cleanse the wound thoroughly before applying the wound vac.
- Use sterile dressings and equipment.
- Change dressings and tubing regularly as per physician’s orders.
- Monitor the patient for signs of infection and report any concerns promptly.
To manage infections:
- Remove the infected dressing and cleanse the wound with an antiseptic solution.
- Apply a new sterile dressing and secure it in place.
- Administer antibiotics as prescribed by the physician.
- Monitor the wound closely for improvement or worsening.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of a wound vac?
A wound vac is used to promote wound healing by creating a negative pressure environment that draws out fluids and stimulates tissue growth.
How often should a wound vac be changed?
The frequency of wound vac changes depends on the type of wound and the amount of drainage. Typically, wound vacs are changed every 2-3 days.
What are the potential complications of wound vac changes?
Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and skin irritation. Proper technique and sterile precautions can minimize these risks.